Recommended Selection and Usage Guide for Standard Steel Doors
SDI 108-23
View PDF
Purpose
To establish guide criteria for the selection and usage of 1-3⁄4″ and 1-3⁄8″ standard steel doors.
Selection
Standard steel doors are classified in four levels: Level 1 – 1-3⁄4″ and 1-3⁄8″ standard duty, Level 2 – 1-3⁄4″ heavy duty, Level 3 – 1-3⁄4″ extra heavy duty and Level 4 – 1-3⁄4″ maximum duty.
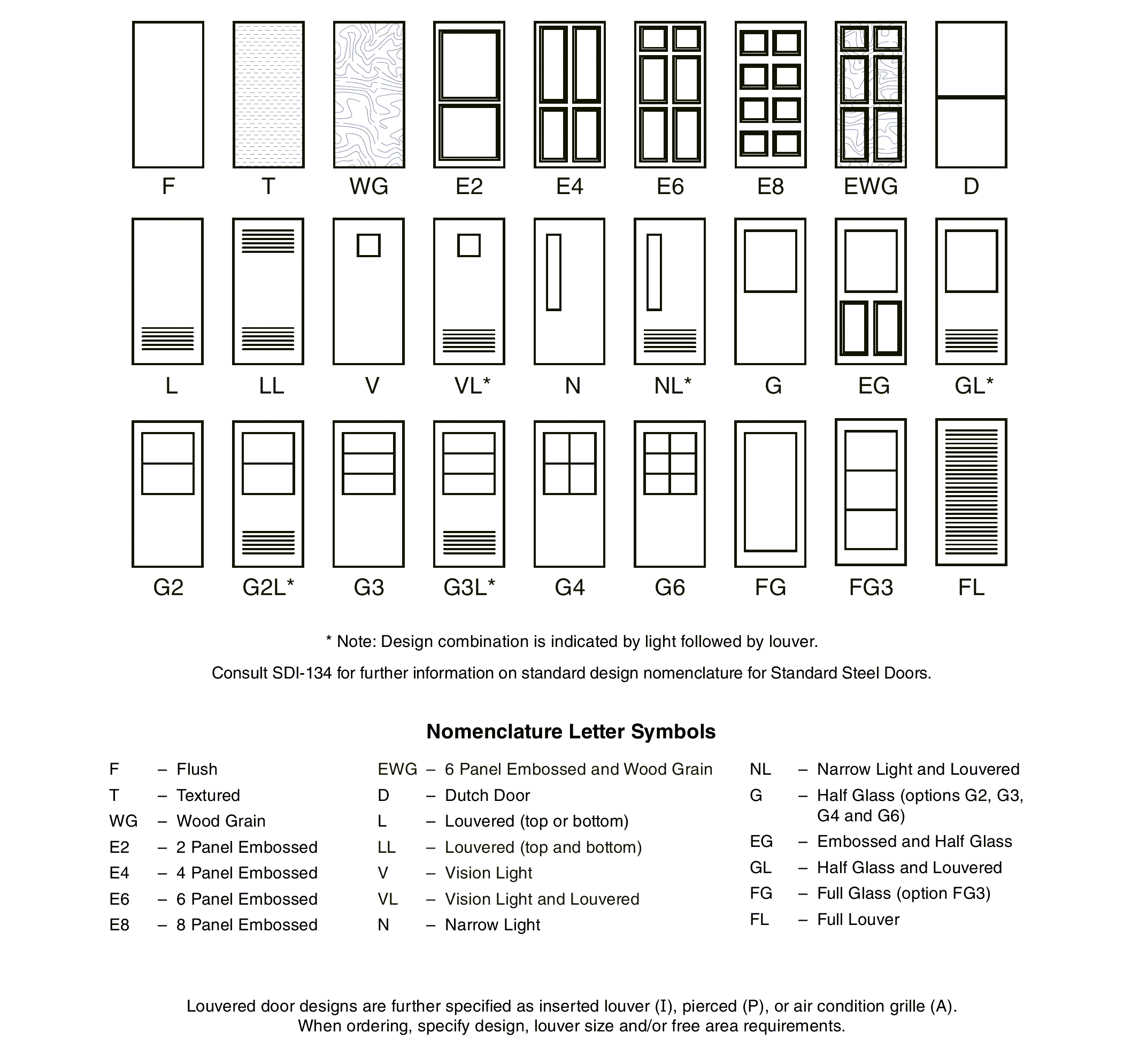
Each of the four levels noted above offer a range of construction models and designs to meet architectural requirements for preference and appearance. The standard steel door construction models are full flush, seamless and, stile and rail.
Recommended minimum gauge requirements for the various levels and models of standard steel doors are indicated in table 1.
Usage
Selection of standard steel doors for general usage is made by analyzing criteria such as frequency of use, including subjection to and degree of possible abuse. Other criteria to be considered in door selection are: conformance to local building codes and fire code regulations; sound attenuation and/or insulation requirements; and architectural design and appearance.
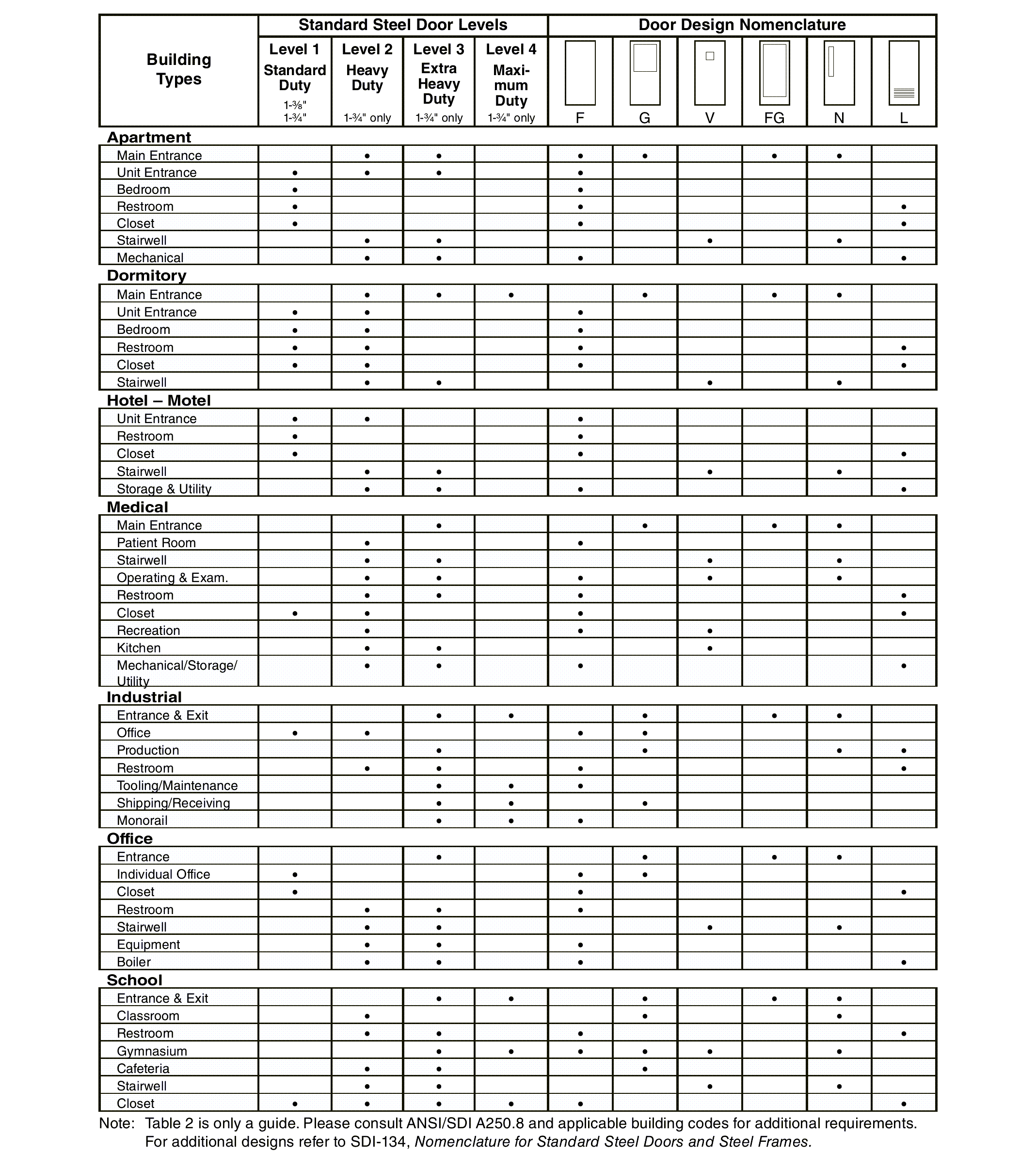
Table 2 is a reference aid matching standard duty, heavy duty, extra heavy duty and maximum duty doors with general usage requirements within the classification of buildings. Where optional door levels and models are indicated, further analysis on an individual job basis is recommended.
When unusual or special door usage conditions are encountered, contact a representative member of the Steel Door Institute for consultation and guidance.
Notes:
- Tolerances – All values which do not carry specific tolerances or are not marked maximum or minimum shall have the following tolerances: Linear dimensions shall be ± 1/16 in. (1.6 mm). Weight or force shall be ± 2%. Angles shall be ± 2 degrees. Where only minus tolerances are given, the dimensions are permitted to be exceeded at the option of the manufacturers.
- Gauge vs. Thickness – While the term gauge is no longer common for defining material thickness it is still used to specify doors and frames for ordering purposes. As such, the terms thickness is used when defining the actual dimension of an item and gauge is used in the context of specifying a particular door or frame.
Table 1 – Standard steel door levels and models
| Level | Model | Full Flush or Seamless | Construction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSG No. | IP in | SI mm | ||||
| 1 | Standard Duty | 1 | 20 | 0.032 | 0.8 | Full Flush |
| 2 | Seamless | |||||
| 2 | Heavy Duty | 1 | 18 | 0.042 | 1 | Full Flush |
| 2 | Seamless | |||||
| 3 | Extra Heavy Duty | 1 | 16 | 0.053 | 1.3 | Full Flush |
| 2 | Seamless | |||||
| 3 | *Stile & Rail | |||||
| 4 | Maximum Duty | 1 | 14 | 0.067 | 1.6 | Full Flush |
| 2 | Seamless | |||||
*Stiles and rails are 16 gauge; flush panels, when specified, are 18 gauge.
For complete standard steel door construction specifications and available sizes, refer to ANSI/SDI A250.8 – Specifications for Standard Steel Doors and Frames (SDI-100) and ANSI/SDI A250.4 – Test Procedure and Acceptance Criteria for Physical Endurance for Steel Doors, Frames, and Frame Anchors.
Table 2 – Suggested door levels and applications
Steel Door Institute Standard Steel Door Design Nomenclature